Laser Scanning: Here’s Everything You Need to Know
Laser scanning has experienced significant growth in recent years as the technology becomes progressively faster, cheaper, and more accurate. The construction industry has led demand for laser scanning, as the technology offers the industry a quick and cost-effective way to capture field data on construction sites.
Although laser scanning has not always been a staple technology in construction, it is slowly becoming irreplaceable. According to POB magazine, overall demand for laser scanning has risen sharply since 2016. In 2016, demand for scanning in the construction industry was only 20%. In 2018, however, demand had risen to 57%.
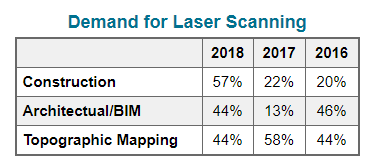
This rapid increase in demand shows just how quickly laser scanning is being adopted in construction. Construction companies are primarily using scanning technology to create more accurate site measurements and support building information modeling (BIM) processes, among other applications. As laser scanning becomes an essential technology in construction, many companies are scrambling to learn how to integrate it into their own projects.
In this post, we will provide a broad overview of laser scanning’s role in the construction industry—explaining how laser scanning works, its various applications, and debunk a few common misconceptions about the technology. Whether you are looking to use laser scanning in your next project or want to learn more about its potential, this guide will provide you with the resources you need to get started.
What Is Laser Scanning?
Before we explore the applications of laser scanning, we’ll first describe how the technology works. Laser scanning, also known as 3D imaging or 3D reverse engineering, is the process of capturing digital information about an object using a non-destructive laser beam. This is achieved by rotating the scanner 360 degrees and connecting the laser beam with various surfaces in the area being scanned. The scanner then uses this information to identify the exact location of objects relative to its position.
The data generated during the scan is called a “point,” and, as the scanner picks up more points, a complete digital representation of the scanned area is formed. This collection of points is known as a point cloud, which project stakeholders can use to capture accurate field data.
While the scanner is collecting these points, it is also creating high-resolution images of the area. These images can be mapped onto point cloud data and used for virtual walk-throughs of the project site. Laser scanning also allows contractors to access scan data that can be updated easily as the project progresses—ideal for site monitoring.
How Does Laser Scanning Help in the Construction Industry?
Laser scanning has many applications in construction because it can capture site conditions accurately while saving companies significant time and money. Here’s a closer look into how laser scanning is being used across the industry:
1. Scanning Helps Update As-Built Documentation
The role of as-built documentation is to provide an accurate representation of field conditions. This is especially important when renovating or maintaining facilities, as stakeholders must have a complete idea of the existing structure before making changes. Scanning facilitates this process—capturing exact measurements of built structures and leaving less room for error than traditional methods of measurement.
Because laser scanning is so precise, project managers can ensure that site measurements and as-built documentation are accurate and up to date. One of the major advantages of laser scanning is its comparatively lower cost and higher accuracy levels than alternative methods.
Putting together as-built documentation is a costly, labor-intensive process when using typical surveying methods—often taking weeks at a time for technicians to complete. With laser scanning, project stakeholders can reduce the time spent measuring site conditions and save money on labor. When updating as-built documentation with laser scanners, stakeholders can benefit from:
- Improved Accuracy – Laser scanners capture every element within a project site, creating a detailed record that can be used for as-built documentation. These measurements are accurate to within an eighth of an inch—producing exact measurements that cannot be created using traditional surveying methods.
- Greater Efficiency – Laser scanning is significantly faster than other surveying techniques. One 3D scanner can capture millions of data points per second—achieving the same results in one day as a team of several technicians could accomplish in a full week.
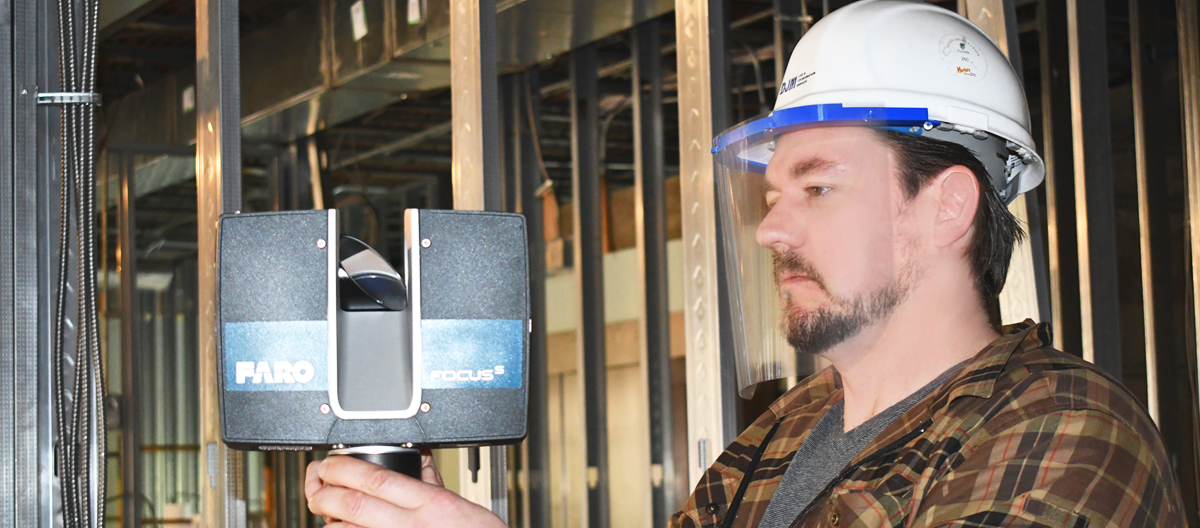

2. Scanning Assists with Site Monitoring
A major advantage of laser scanning is its ability to capture site conditions quickly and accurately—proving useful when monitoring construction progress. With the use of scanning technology, project managers can refer to virtual models of project structures to monitor site progress remotely. The site monitoring capabilities offered by laser scanning help stakeholders in the following ways:
- Increased Transparency – By using 3D scanning to create a digital representation of the project site, transparency can be ensured. This is because stakeholders can view the same information about the project—reducing miscommunication and boosting accountability.
- Better Safety – There are many risks associated with site work, as construction sites are often dangerous—accounting for over 18% of all fatal occupational injuries. By taking advantage of laser scanning to create a digital model, stakeholders can avoid the risks associated with being physically present on the project site.
- Ability to Create Audit Trails – Laser scanning can also be useful when creating audit trails. By converting scan data into a digital model of the project site, stakeholders can record any changes made to the site. This information is valuable when performing future audits and defending against potential defect claims.
- Significant Cost Savings – When compared to traditional methods of surveillance, laser scanning is significantly cheaper. This is because scanning allows developers to spend less time recording site data—meaning fewer labor hours and reduced project costs.

3. Scanning Facilitates Renovations, Retrofits, and Facility Maintenance
During renovations, project managers are often handed inaccurate or outdated as-built documentation—leaving them with a poor understanding of how the building is laid out. Basing project plans on inaccurate blueprints can lead to project delays and change orders, driving up overall costs. By using laser scanning at the beginning of a retrofit or renovation project, project managers can benefit from:
- BIM Coordination Capabilities – Laser scanners capture exact 3D virtual tours of the project site. Project managers can use site tours to take exact measurements virtually—eliminating the need to be physically present at the project site. With this data, BIM drafters can draw equipment and trade-specific elements that represent the actual size needed for installation. This ensures that manufactured components fit perfectly, streamlining renovation projects.
- Easier Facility Maintenance – Laser scanners can also create permanent as-built records for owners and facility managers. This data contains a high level of detail and can speed up the process of fixing, upgrading, and replacing equipment. Detailed information about facility space can also help facility professionals determine the size, use, location, and contents of assets in their building.
- Clash Detection Software – To ensure that there are no overlapping components, BIM teams can use a process known as “Scan to BIM” to clash detect new equipment plans. After technicians have taken a 3D scan of the project site and drafters have finished modeling new equipment, these two pieces of information can be overlaid to ensure that equipment is placed correctly.
- Less Rework, Fewer Change Orders – By verifying the site and ensuring that new equipment can be installed correctly, stakeholders can avoid potential rework, which can negatively affect the project’s budget. By taking the time to expose inaccuracies during preconstruction, stakeholders can keep on schedule and stay within budget.
Correcting Common Misconceptions About Laser Scanning
As an emerging technology in construction, laser scanning has generated a lot of discussion among construction professionals. Among this discussion, a few prominent misconceptions about the technology have emerged. What are people getting wrong about laser scanning?
Myth 1: It’s expensive.
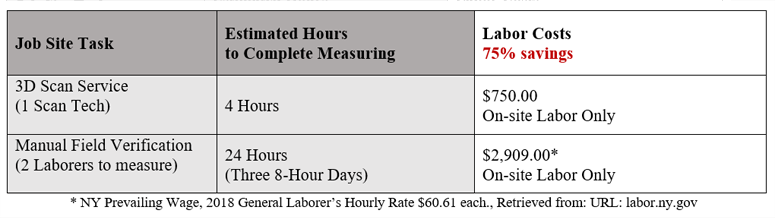
Although laser scanning equipment can be expensive, purchasing scanning services is an affordable option for many construction companies. For example, in 2018, DJM was approached by a general contractor managing a Manhattan skyscraper project who requested measurements of the building. The contractor had received an initial quote from one of the skilled trade teams working on the project, and was looking for a cheaper option.
The initial estimate stated it would cost $2,909 and require two skilled trade workers to work three eight-hour long sessions to take the measurements. After contacting DJM, the contractor was surprised to learn our scanning team could take the measurements in four hours, and that it would only cost $750 for labor. In this case, hiring DJM to scan saved over $2,000 on labor alone.
Myth 2: Scans take a long time to complete.
Yet another misconception about laser scanning is that it takes a long time to complete a scan. With today’s connectivity, technicians can process scans while still on the field. Scanning and processing can be performed together—allowing drafters to begin drafting while the scanning team is still on the site taking measurements.
Myth 3: Scans can only be used for measuring.
Although scanning is often used as a tool for measurement, it has broader applications in the construction industry. Because of the pandemic, remote coordination has became a necessity due to travel restrictions, which make it difficult for contractors to continue working. With scan data, remote coordination becomes possible—making it easy for teams to access project sites through virtual walkthroughs.
Read More About Laser Scanning
Want to learn more about laser scanning technology and its applications throughout the construction lifecycle? Here are several articles and case studies about construction companies using laser scanning to boost their bottom line:
- FARO Technologies – Watch this video to learn how 3D scanning was used to renovate the Hutchinson Regional Medical Center—saving up to 4 months on the project schedule.
- Construction Executive – Learn more about how scanning is being used throughout the construction industry in this article published by one of our project managers.
- For Construction Pros – Read one of our case studies to learn how we fully repaired a manufacturing facility using scanning technology after it was damaged in a fire.
Get Started with Scanning
Although the construction industry has been slow to adopt laser scanning, the technology is becoming the norm on project sites for its efficiency, accurate measurements, and cost savings. To learn more about scanning technology and how it can help with your next project, download our free e-book:




