How Accurate Is 3D Scanning? Here’s Everything You Need to Know
Poor data costs the construction industry up to $88.69 billion per year, says FMI and Autodesk. If you rely on inaccurate data, you risk creating rework, delays, and budget overruns. How can you avoid these risks and improve the quality of your data?
One tool helping contractors collect more accurate data is 3D scanning. The technology uses laser beams to capture digital information about the surrounding area. Its accuracy allows contractors to better understand site conditions and eliminate rework.
Below, we look at how accurate 3D scanning is and describe the difference between accuracy and resolution. Plus, we’ll give you tips on choosing the right accuracy level for your next project.
How Accurate is 3D Scanning?
When used correctly, 3D scanners produce measurements with an accuracy of +/- 1 mm. The accuracy of these measurements eliminates the need to return to the field.
3D scanning is also visually impactful. Once the scans are converted into digital files, you can use these files to virtually walk through your job site. You can also take measurements down to the millimeter within the file. This allows you to access information about the distance, area, and volume of the space whenever you need it, and from any location.
Want to learn how laser scanning can help you save time and money on projects? Download our e-book, The Beginner’s Guide to 3D Scanning.
3D Scanning Accuracy vs Resolution: What’s the Difference?
Confused about the difference between accuracy and resolution, and how each applies to 3D scanning? Here’s a quick breakdown:
What Is Accuracy?
Accuracy is how close the 3D scanner’s measurements are to the true size of the object. For example, if a cube has a width of 50.50 mm and a 3D scanner captures its width as 50.48 mm, the scan is relatively accurate. This is because the measurement comes close to the true dimensions of the cube. If your measurements must have a low margin of error, you should increase the accuracy of your scans.
Accuracy is different from precision, which shows how repeatable a measurement is. The graphic below illustrates the difference between accuracy and precision:
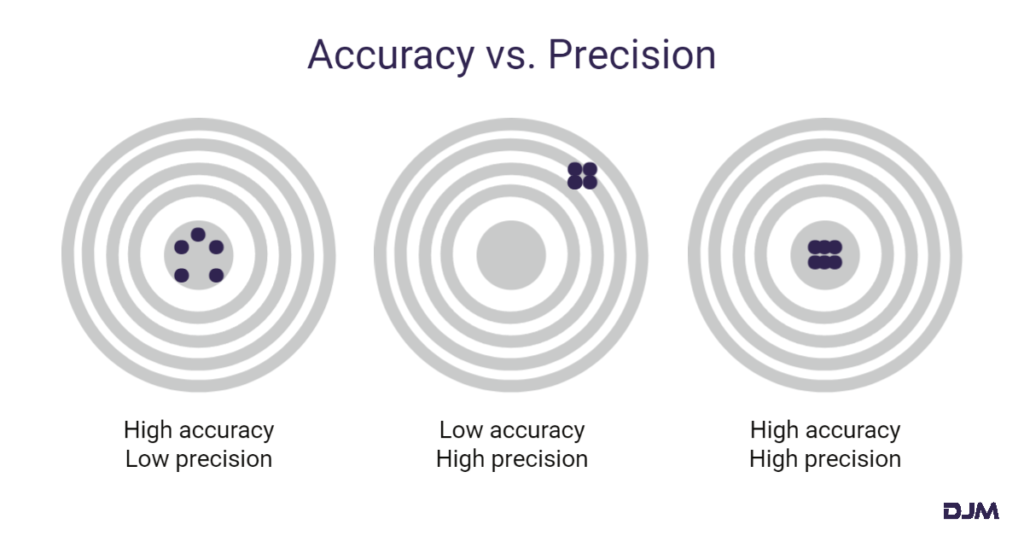
What Is Resolution?
Resolution is the distance between data points captured by the 3D scanner. If the data points are dense and close together, then the resolution is high, and the resulting scan will be crisp. If you need to capture fine architectural details or small objects, then you should increase the resolution of your scans.
What Level of Accuracy Does Your Project Need?
How accurate should your scans be? It depends on the minimum level of accuracy needed to complete your project. If you want to monitor construction progress, then you probably don’t need measurements accurate down to the millimeter. A less accurate scan will still allow you to track construction progress.
Some projects require higher levels of accuracy, such as floor flatness reports or renovations. In these cases, the margin of error must be small, and scans should be accurate down to the millimeter. You can consult with a 3D scanning technician to determine the right level of accuracy for your individual project needs.
Improve Your Project’s Accuracy with 3D Scanning
Although the construction industry has been slow to adopt 3D scanning, the technology is becoming the norm on projects for its accuracy, efficiency, and cost-savings. To learn more about laser scanning and how it can help with your next project, download our free e-book:




